Reactor For Different Kinds Of Resins | JCT Machinery
 Oct 17,2024
Oct 17,2024
 JCT
JCT
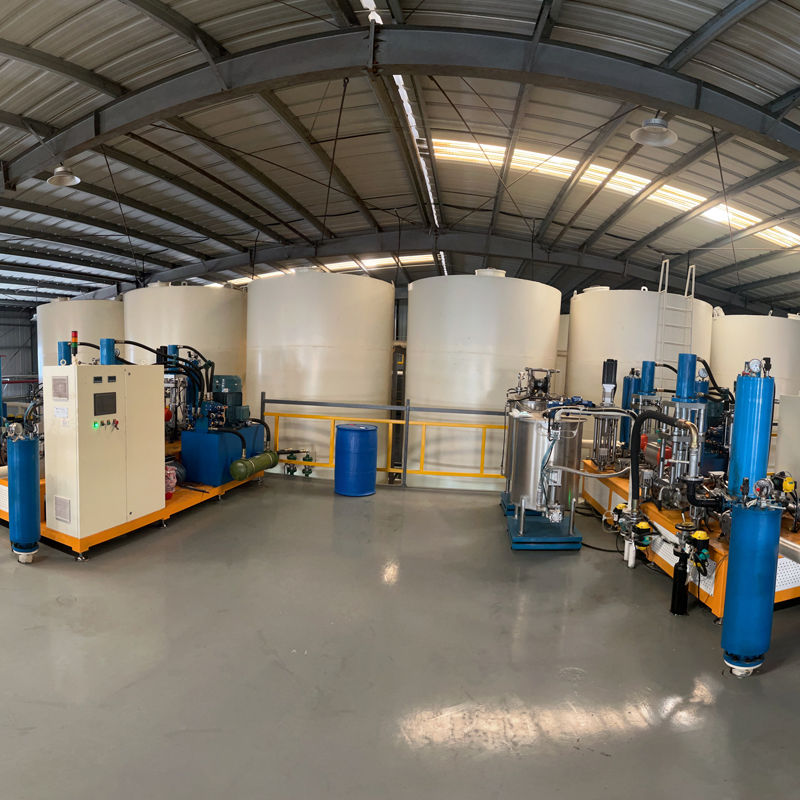
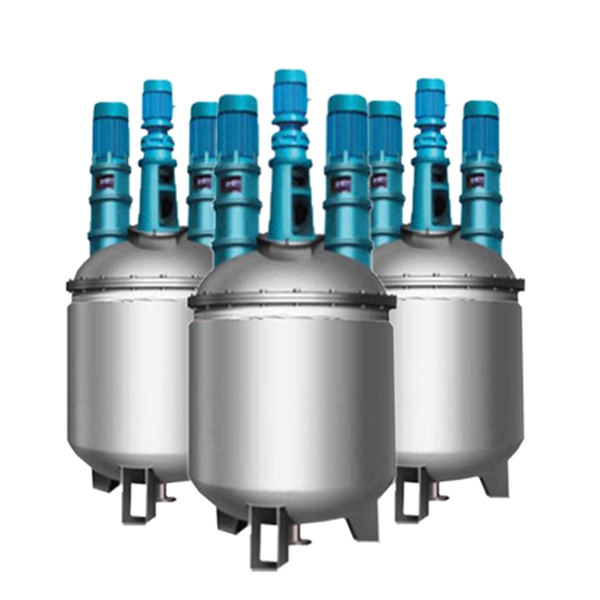
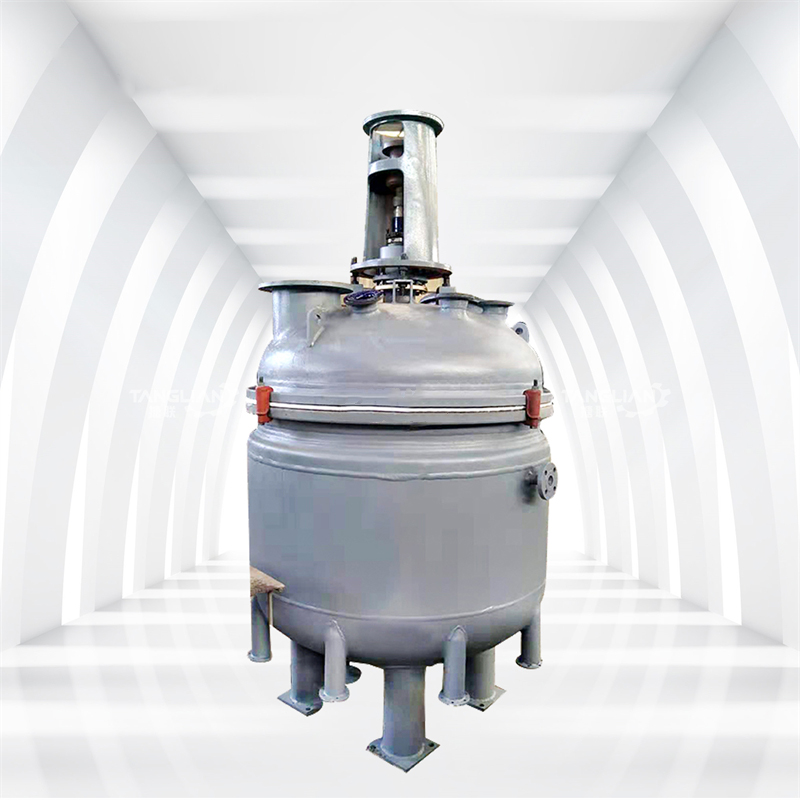
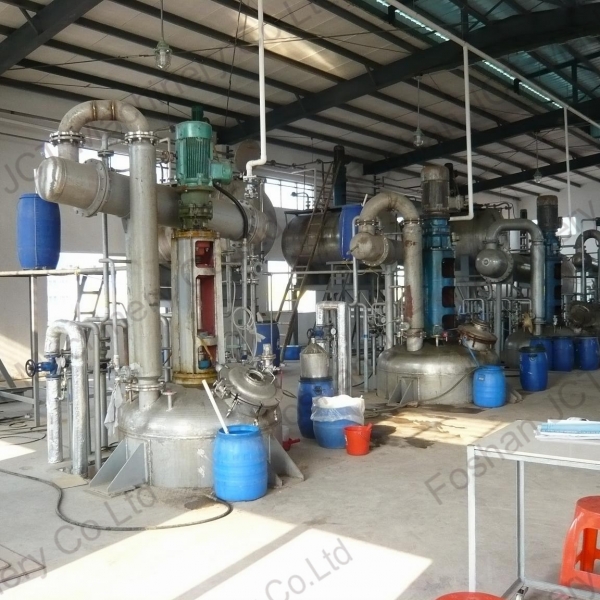
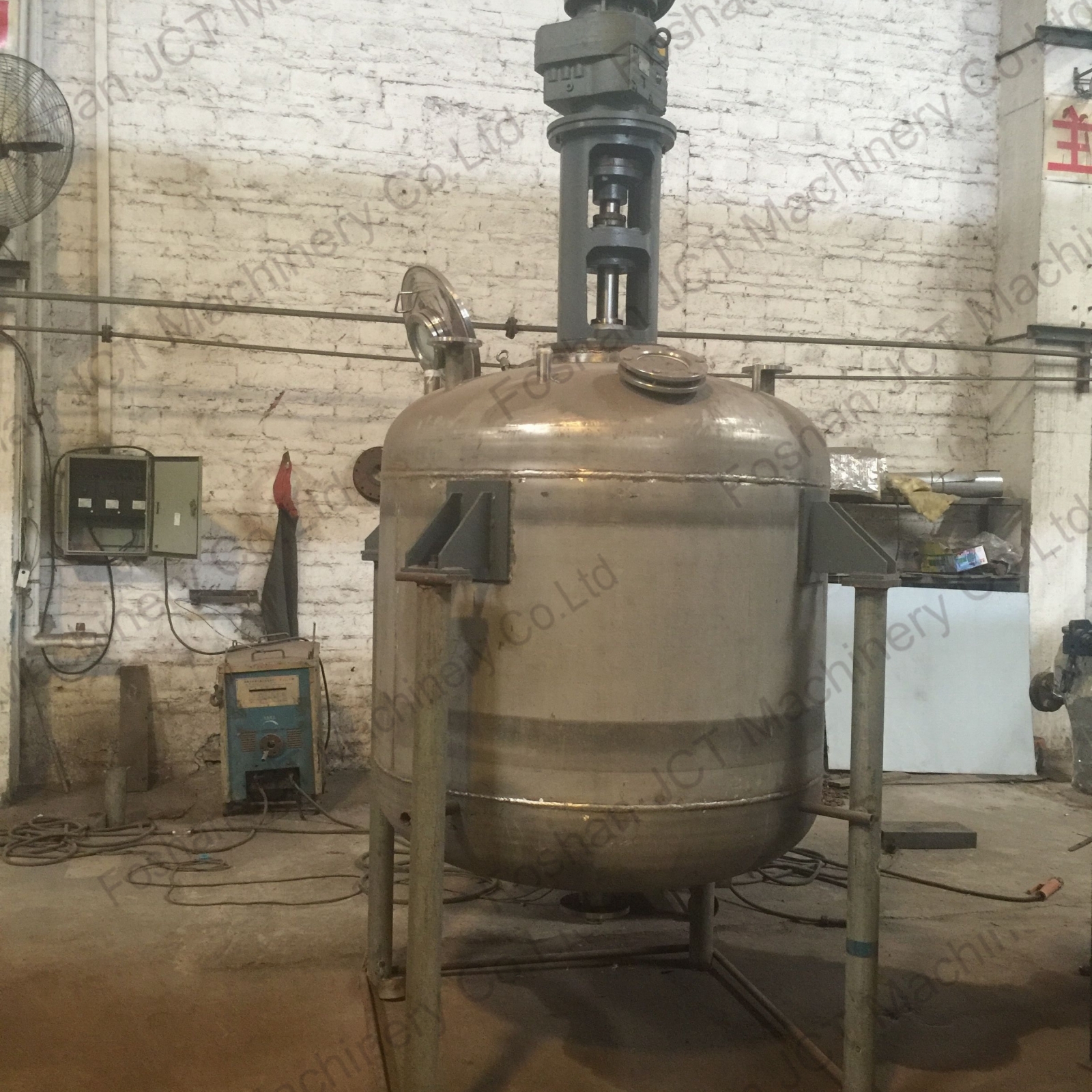
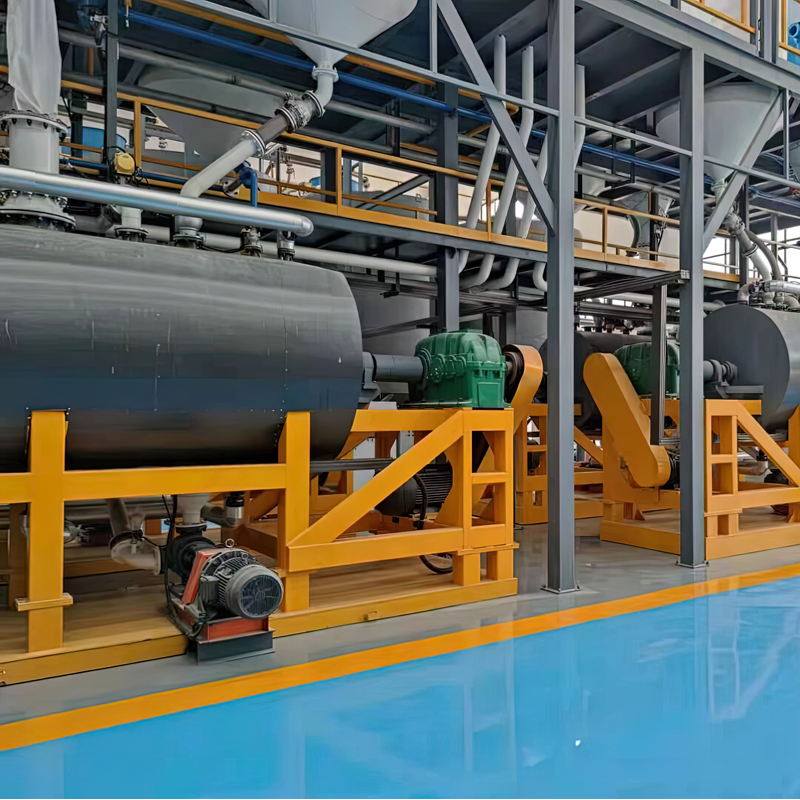
The versatility of reactor makes it the main equipment in equipment in resin production process. It ensures the reaction quality and performance of different resins by precisely controlling the reaction temperature, pressure, stirring rate and time.
Common Resins Produced By Reactor
1. Unsaturated Polyester Resin
- Production Process: Unsaturated polyester resin is prepared by polycondensation of dibasic acid and diol in a reactor. The production process also requires the addition of a crosslinking agent under certain conditions.
- Application: Unsaturated polyester resin is commonly used in fiberglass, composite materials, coatings, adhesives and other fields.
2. Epoxy Resin
- Production Process: Epoxy resin is mainly produced by polycondensation of epichlorohydrin and bisphenol A or other polyols in a reactor. The reaction process requires precise control of temperature and stirring speed.
- Application: It is widely used in coatings, adhesives, electronic packaging materials, composite materials and structural bonding, and is widely used due to its good mechanical properties and chemical resistance.
3. Phenolic Resin
- Production Process: It is formed by condensation of phenol and formaldehyde under the action of acidic or alkaline catalysts. The reaction process can select thermoplastic or thermosetting products as needed, and the temperature and pH control in the reactor is crucial.
- Application: Commonly used in the manufacture of high-temperature resistant electrical insulation materials, molding materials, wear-resistant laminates, adhesives, etc.
4. Polyurethane Resin
- Production Process: Polyurethane resin is produced by the reaction of polyols and isocyanates in a reactor. The properties of the resin can be controlled by adjusting the reaction temperature, pressure and stirring speed. The production process of polyurethane resin usually involves the use of different additives and catalysts.
- Application: Widely used in soft foam, hard foam, coatings, elastomers, sealants, adhesives, sole materials and other fields.
5. Acylic Resin
- Production Process: It is produced by free radical polymerization of acrylic acid and its ester monomers. In the reactor, the reaction temperature and the choice of initiator have an important influence on the molecular weight and properties of the final resin.
- Application: Commonly used in coatings, adhesives, textile finishing agents, inks and building decoration materials.
6. Ester Resin (such as Alkyd Resin)
- Production Process: It is produced by polycondensation of fatty acids with polyols, dibasic acids or anhydrides in a reactor. Reactor provides uniform heating and stirring to ensure the smooth progress of the esterification reaction.
- Application: Mainly used in the coating and paint industry, alkyd resins are widely used in architectural coatings and anti-corrosion coatings due to their excellent adhesion, weather resistance and gloss retention.
7. Amide Resin
- Production Process: Produced by the reaction of fatty acids and polyamine compounds. Reactor can achieve directional synthesis of the resin while controlling temperature, pressure and reaction time.
- Application: Used in coatings, inks and paper coatings, with water resistance, chemical resistance and other properties.
8. Urea-formaldehyde Resin
- Production Process: It is generated by condensation reaction of urea and formaldehyde in the reactor, and an alkaline catalyst is usually used to adjust the reaction rate. By controlling the reaction conditions, the fluidity and curing characteristics of the resin can be adjusted.
- Application: Widely used in the manufacture of adhesives in the wood industry such as plywood, particleboard, fiberboard, and also used in coatings and molding materials.
9. Ethylene-vinyl Acetate Resin (EVA Resin)
- Production Process: Prepared by copolymerization of ehtylene and vinyl acetate monomers. Reactor provides an environment for controlling the reaction temperature and pressure to ensure the stability of the molecular structure of the resin.
- Application: Commonly used in hot melt adhesives, foam materials, shoe materials and packaging materials, with good flexibility and strong weather resistance.




















 CN
CN
 HOME
HOME Alkyd Resin Production Details | JCT Machinery
Alkyd Resin Production Details | JCT Machinery  You May Also Like
You May Also Like





 Tel
Tel
 Email
Email
 Address
Address










