Grease Manufacturing Process | JCT Machinery
 Dec 01,2023
Dec 01,2023
 JCT
JCT
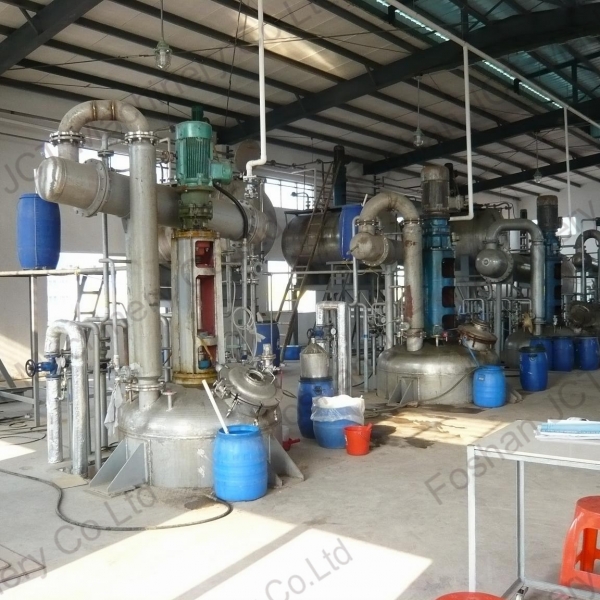
Grease manufacturing process involves combining a thickening agent, a base oil and additives. Grease is a semi-solid lubricant used to reduce frictiono and wear between moving parts, providing lubrication in various applications.
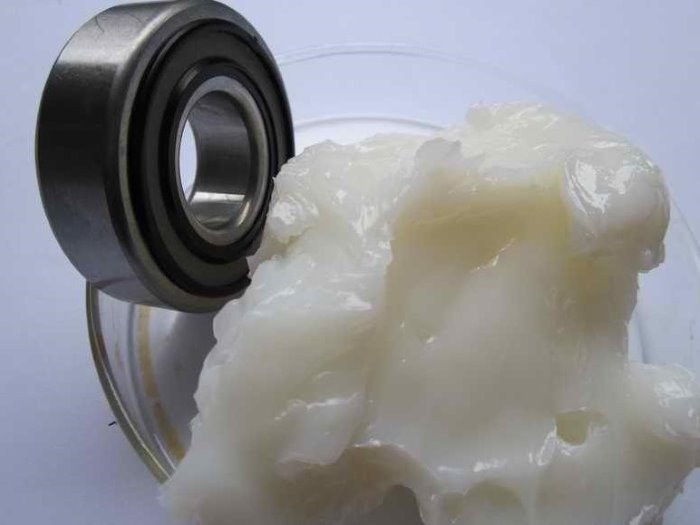
Grease Manufacturing Process
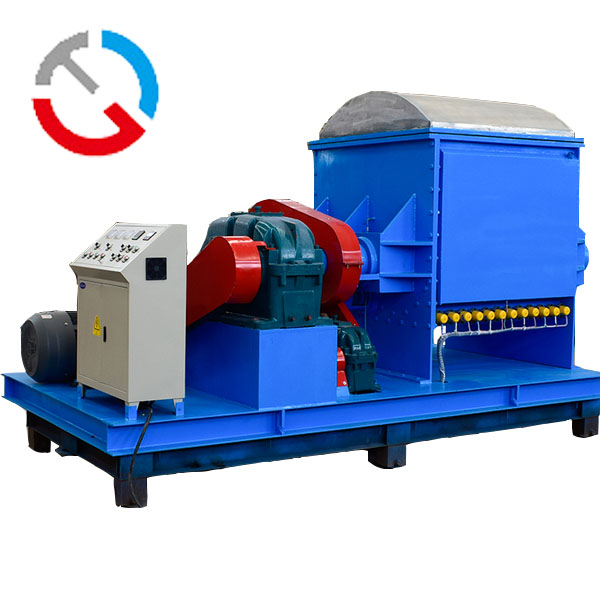
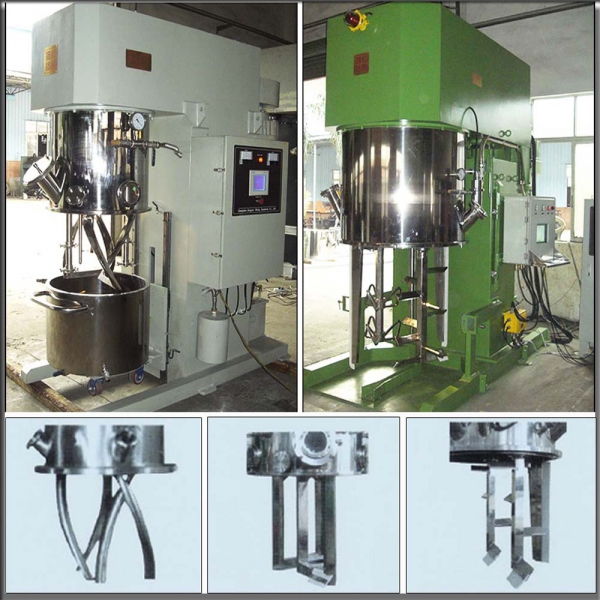
1. Mixing the Base Oil and Thickening Agent
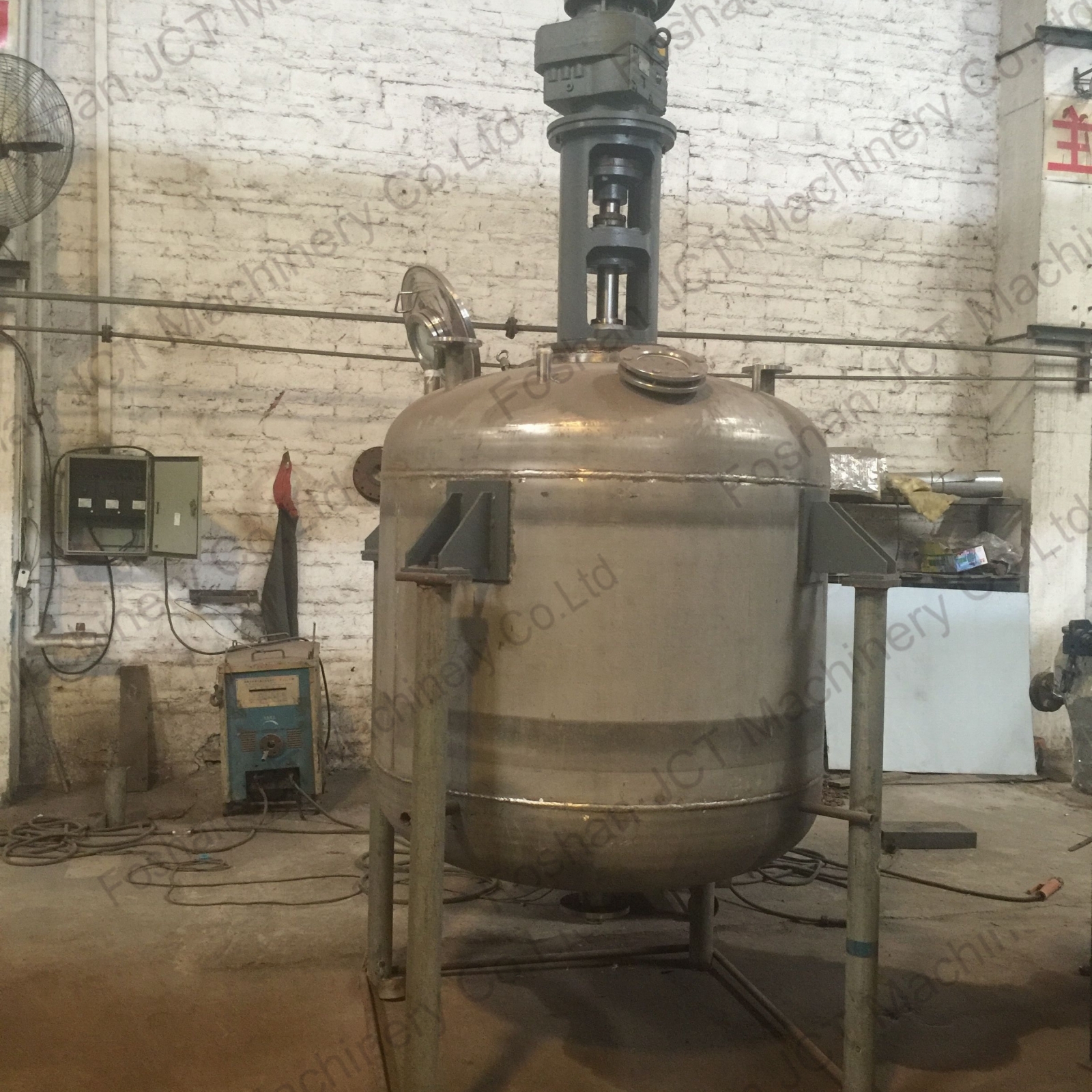
The selected base oil and thickening agent are mixed together. This process, known as saponification, involves reacting the thickening agent with the base oil to form the soap structure that thickens the grease. This step may be performed in a reactor.
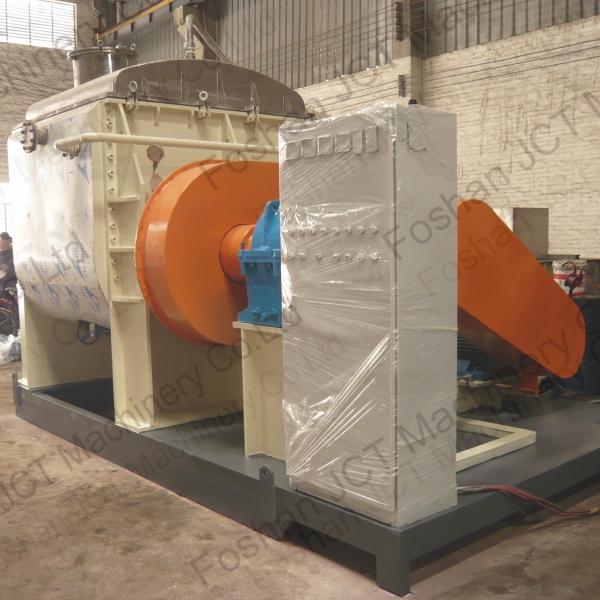
2. Addition of Additives
Various additives are incorporated to enhance the performance of the grease. Common additives include:
• Antioxidants: Prevent oxidation of the grease.
• Anti-wear agent: Reduce friction and wear.
• Extreme pressure (EP) additives: Provide protection under high pressure conditions.
• Corrosion inhibitors: Protact against corrosion.
• Viscosity modifiers: Control the viscosity of the grease over a range of temperatures.
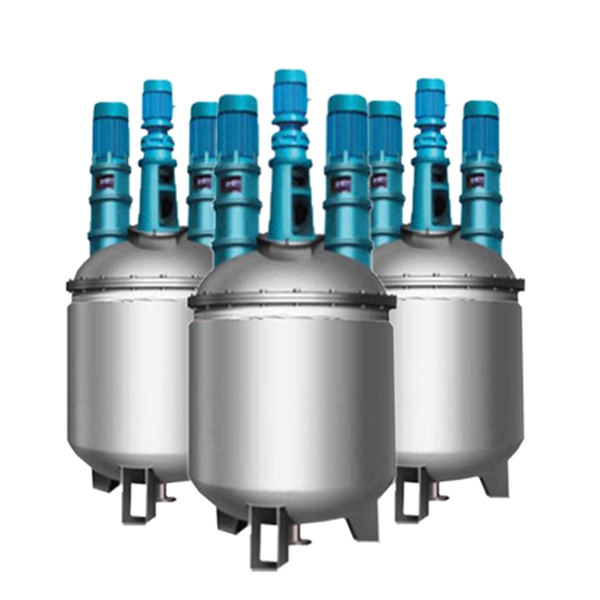
3. Mixing and Homogenization
The mixture undergoes further mixing and homogenizaion to ensure uniform distribution of the thickener, base oil and additives. This step helps achieve consistent product quality.
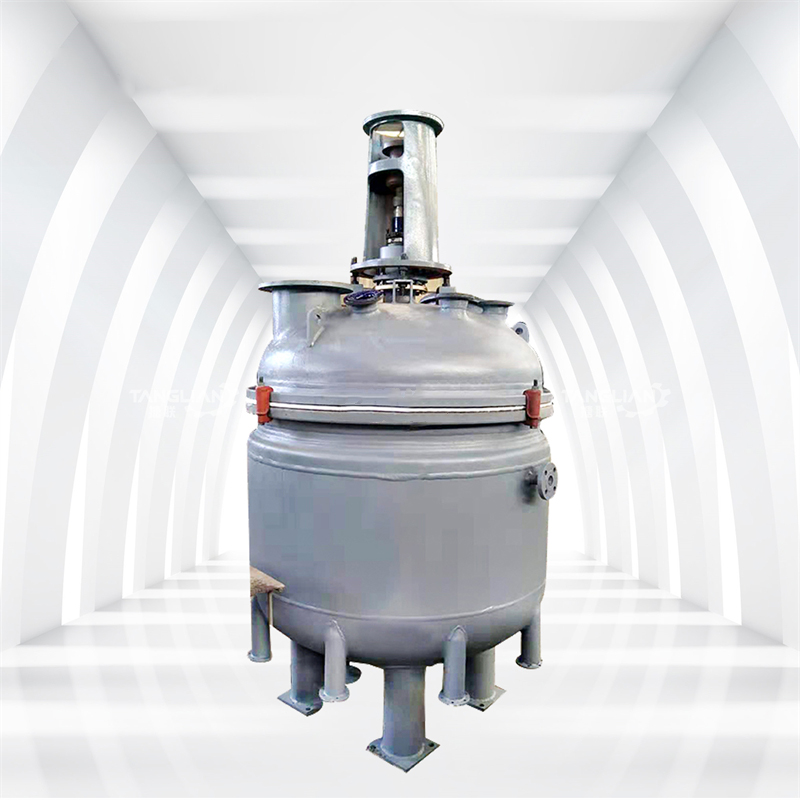
4. Testing and Quality Control
The grease is subjected to various tests to ensure it meets quality standards. Common tests include penetration tests, dropping point determination, shear stability tests and other performance evaluations.



















 CN
CN
 HOME
HOME What Is Plasticine Used For? | JCT Machinery
What Is Plasticine Used For? | JCT Machinery  You May Also Like
You May Also Like





 Tel
Tel
 Email
Email
 Address
Address










