What Is Reactor In Pharmaceutical? | JCT Machinery
 Dec 05,2023
Dec 05,2023
 JCT
JCT
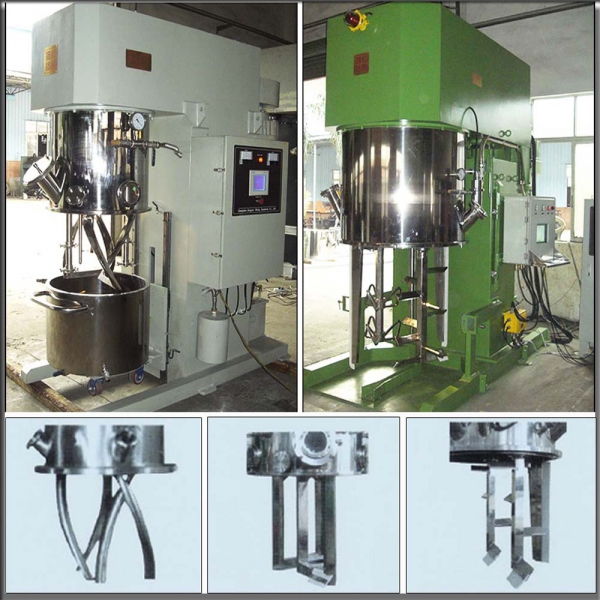
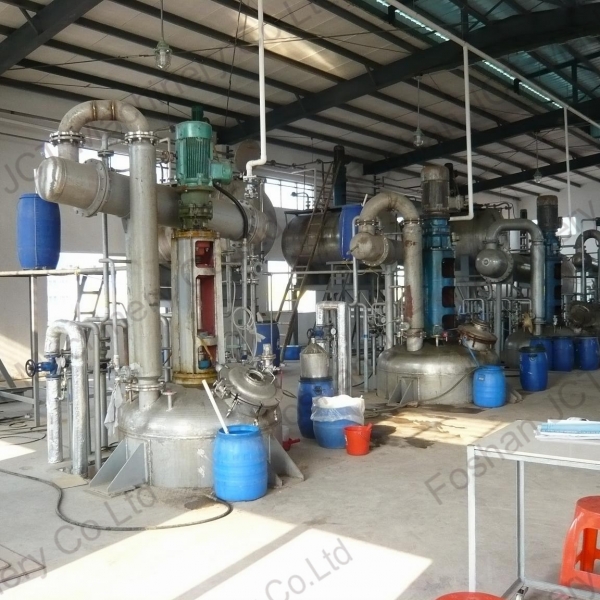
In the pharmaceutical industry, a reactor refers to a vessel or container used for various chemical processes, typically involving the synthesis or production of pharmaceutical compounds. These reactors play a crucial role in pharmaceutical manufacturing, allowing for precise control of reaction conditions, such as temperature, pressure, and mixing, to ensure the desired chemical transformations.
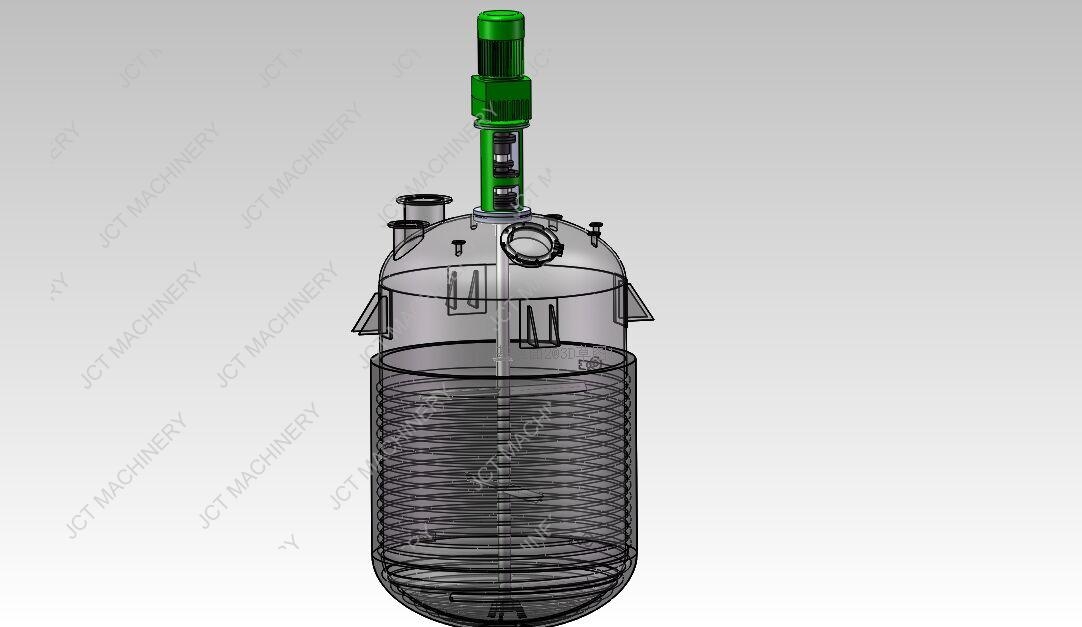

1. Batch Reactor
Bat Reactor is vessel used for small-scale production where a specific quantity of raw materials is charged into the reactor, and the reaction is allowed to proceed until completion. Batch reactors are suitable for producing limited quantities of pharmaceutical products.
2. Continuous-Flow Reactor
Continuous-flow reactor, also known as continuous stirred-tank reactor (CSTR) or plug-flow reactor, operates continuously, with reactants continuously fed into the reactor, and products continuously withdrawn. It is suitable for large-scale production with a continuous flow of raw materials.
3. Pressure Reactor
Some pharmaceutical reactions require elevated pressures to achieve specific chemical transformations. Pressure reactor, designed to withstand high pressure, is used for such processes.
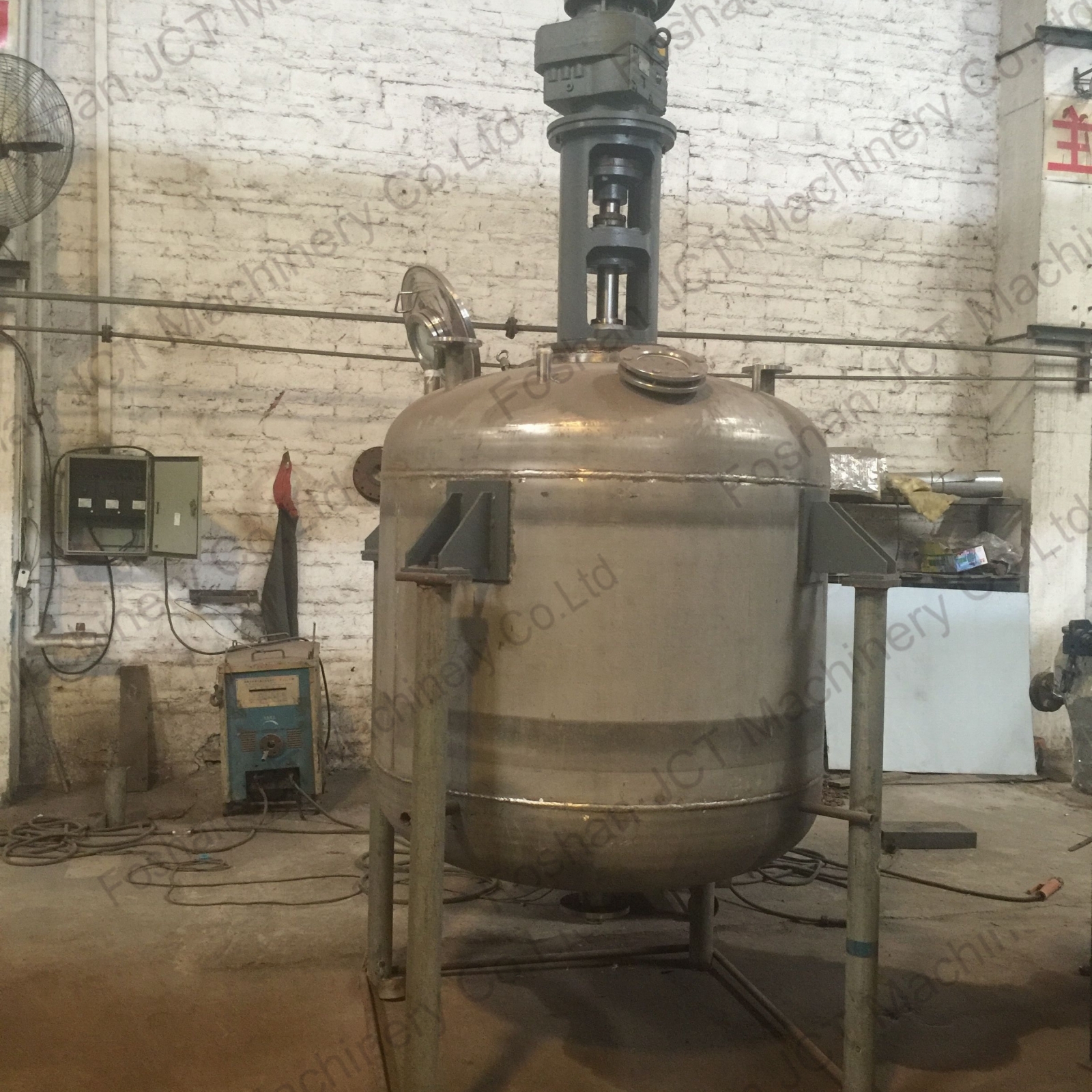
4. Jacketed Reactor
Jacketed reactor has a double-walled structure with an outer jacket through which temperature-controlling fluids (such as hot or cold water or oil) can circulate. This allows precise control of the reaction temperature.
5. High-Pressure Reactor
High-pressure reactor is designed to handle reactions that require pressures higher than atmospheric pressure. It is commonly used in the synthesis of certain pharmaceuticalintermediates.
6. Hydrogenation Reactor
Hydrogenation reactor is employed for reactions involving the addition of hydrogen to organic compounds. They are crucial in the synthesis of various pharmaceuticals, including the reduction of functional groups.
7. Glass Lined Reactor
Glass-lined reactor has a protective layer of glass on the inner surface of the reactor, providing corrosion resistance. They are used for processes hat involve corrosive substances.
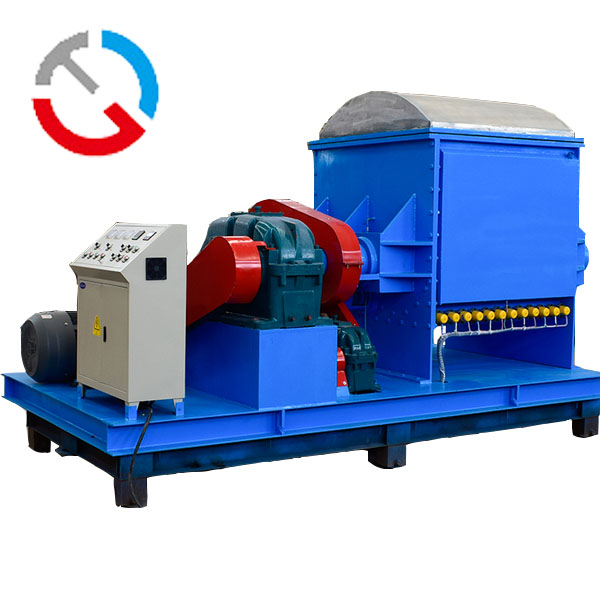
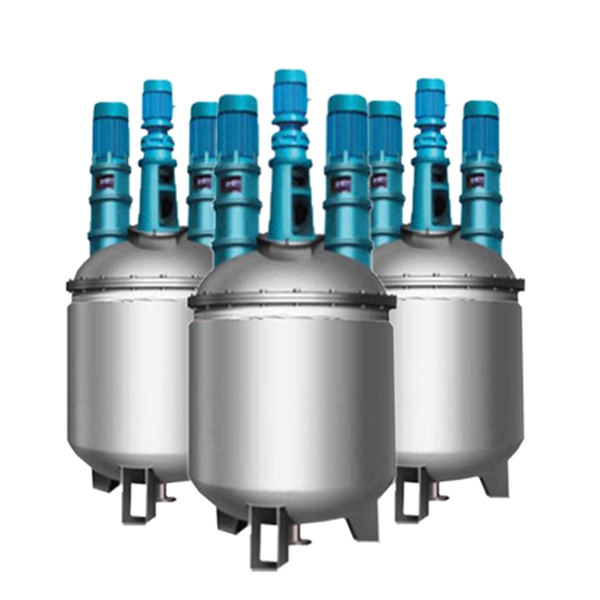
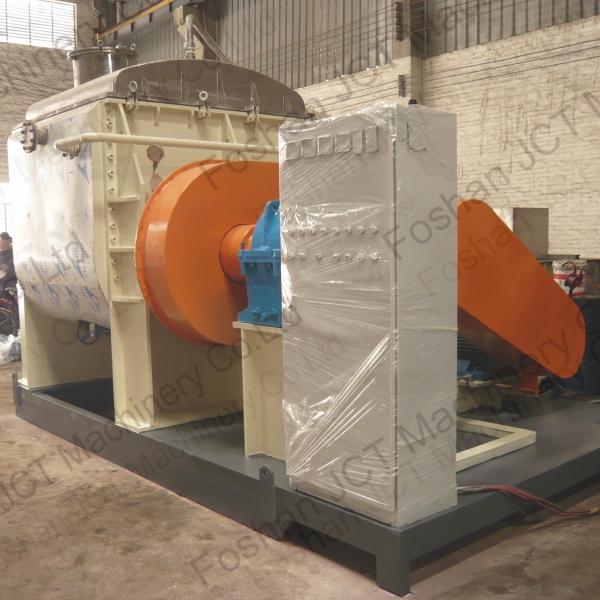
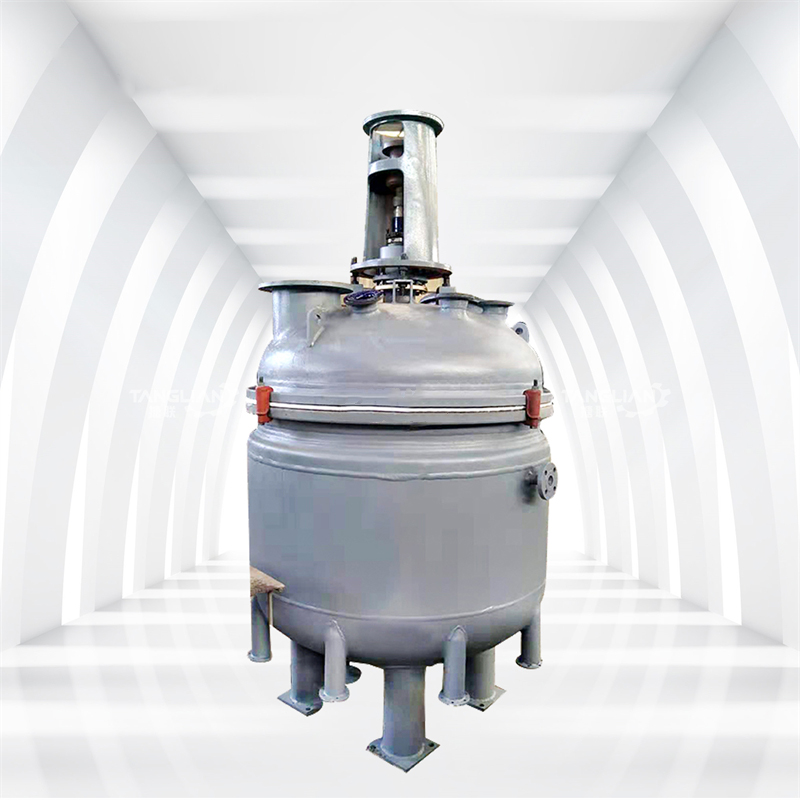



















 CN
CN
 HOME
HOME What Is Resin Manufacturing Process? | JCT Machinery
What Is Resin Manufacturing Process? | JCT Machinery  You May Also Like
You May Also Like





 Tel
Tel
 Email
Email
 Address
Address










